Tag Archives: leetcode
C# || How To Determine When A Fresh Orange Becomes Rotten Using C#

The following is a module with functions which demonstrates how to determine when a fresh orange becomes rotten using C#.
1. Oranges Rotting – Problem Statement
You are given an m x n grid where each cell can have one of three values:
- 0 representing an empty cell,
- 1 representing a fresh orange, or
- 2 representing a rotten orange.
Every minute, any fresh orange that is 4-directionally adjacent to a rotten orange becomes rotten.
Return the minimum number of minutes that must elapse until no cell has a fresh orange. If this is impossible, return -1.
Example 1:
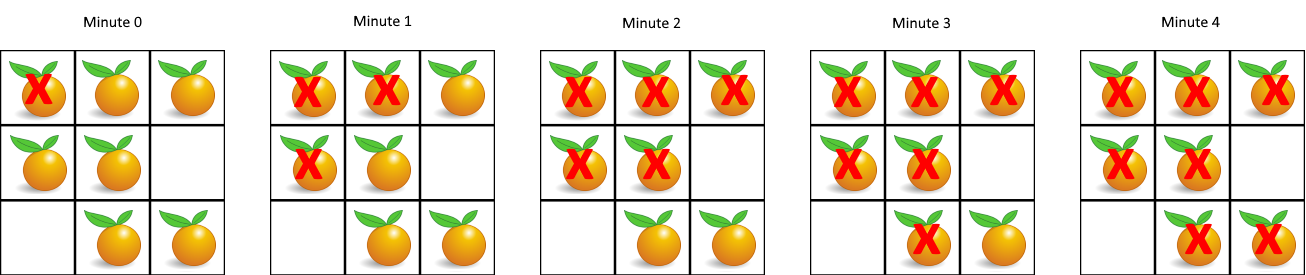
Input: grid = [[2,1,1],[1,1,0],[0,1,1]]
Output: 4
Example 2:
Input: grid = [[2,1,1],[0,1,1],[1,0,1]]
Output: -1
Explanation: The orange in the bottom left corner (row 2, column 0) is never rotten, because rotting only happens 4-directionally.
Example 3:
Input: grid = [[0,2]]
Output: 0
Explanation: Since there are already no fresh oranges at minute 0, the answer is just 0.
2. Oranges Rotting – Solution
The following is a solution which demonstrates how to determine when a fresh orange becomes rotten.
This solution uses Breadth First Search when looking for fresh cells to turn rotten.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 |
// ============================================================================ // Author: Kenneth Perkins // Date: Oct 29, 2021 // Taken From: http://programmingnotes.org/ // File: Solution.cs // Description: Demonstrates how to determine rotten oranges // ============================================================================ public class Solution { public int OrangesRotting(int[][] grid) { var EMPTY = 0; var FRESH = 1; var ROTTEN = 2; var elapsed = 0; var freshCount = 0; var queue = new Queue<KeyValuePair<int, int>>(); // Get fresh cell count and rotten cell coordinates for (int row = 0; row < grid.Length; ++row) { for (int col = 0; col < grid[row].Length; ++col) { if (grid[row][col] == FRESH) { ++freshCount; } else if (grid[row][col] == ROTTEN) { queue.Enqueue(new KeyValuePair<int, int>(row, col)); } } } // Search directions var directions = new List<KeyValuePair<int, int>>() { // Right new KeyValuePair<int, int>(0, 1), // Left new KeyValuePair<int, int>(0, -1), // Top new KeyValuePair<int, int>(-1, 0), // Bottom new KeyValuePair<int, int>(1, 0), }; // Look for fresh cells to turn rotten while (queue.Count > 0) { for (var itemCount = queue.Count; itemCount > 0; --itemCount) { var current = queue.Peek(); queue.Dequeue(); // Get the coordinates of the rotten cell var row = current.Key; var col = current.Value; // Search right, left, top, bottom to see if a fresh cell can become rotten foreach (var direction in directions) { var newRow = row + direction.Key; var newCol = col + direction.Value; // If the cell is fresh in this direction, make it rotten if (IsValidCell(grid, newRow, newCol) && grid[newRow][newCol] == FRESH) { grid[newRow][newCol] = ROTTEN; queue.Enqueue(new KeyValuePair<int, int>(newRow, newCol)); --freshCount; } } } // Increment elapsed time if (queue.Count > 0) { ++elapsed; } } return freshCount > 0 ? -1 : elapsed; } private bool IsValidCell(int[][] grid, int row, int col) { return row >= 0 && row < grid.Length && col >= 0 && col < grid[row].Length; } }// http://programmingnotes.org/ |
QUICK NOTES:
The highlighted lines are sections of interest to look out for.
The code is heavily commented, so no further insight is necessary. If you have any questions, feel free to leave a comment below.
Once compiled, you should get this as your output for the example cases:
4
-1
0
C# || 3Sum Closest – How To Get 3 Numbers In Array Closest Equal To Target Value Using C#

The following is a module with functions which demonstrates how to get 3 numbers in an array closest equal to target value using C#.
1. 3 Sum Closest – Problem Statement
Given an integer array nums of length n and an integer target, find three integers in nums such that the sum is closest to target.
Return the sum of the three integers.
You may assume that each input would have exactly one solution.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [-1,2,1,-4], target = 1
Output: 2
Explanation: The sum that is closest to the target is 2. (-1 + 2 + 1 = 2).
Example 2:
Input: nums = [0,0,0], target = 1
Output: 0
2. 3 Sum Closest – Solution
The following is a solution which demonstrates how to get 3 numbers in an array closest equal to target value.
This solution uses the two pointer technique to find combinations.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 |
// ============================================================================ // Author: Kenneth Perkins // Date: Oct 28, 2021 // Taken From: http://programmingnotes.org/ // File: Solution.cs // Description: Demonstrates how to get 3 numbers closest to target value // ============================================================================ public class Solution { public int ThreeSumClosest(int[] nums, int target) { var result = 0; // Keep track of the solution closest to the target var closestDifference = int.MaxValue; // Sort the array Array.Sort(nums); // Loop through numbers for (int index = 0; index < nums.Length; ++index) { // Skip duplicates if (index > 0 && nums[index] == nums[index - 1]) { continue; } // Find 3 sum combination closest to the target value var startIndex = index + 1; var endIndex = nums.Length - 1; while (startIndex < endIndex) { // Get the sum var sum = nums[index] + nums[startIndex] + nums[endIndex]; // Determine how close the sum is to the target value var difference = Math.Abs(target - sum); if (difference < closestDifference) { closestDifference = difference; result = sum; } // An exact match is found, exit if (difference == 0) { break; // Sum is less than target } else if (sum < target) { ++startIndex; // Sum is greater than target } else { --endIndex; } } // An exact match is found, exit if (closestDifference == 0) { break; } } return result; } }// http://programmingnotes.org/ |
QUICK NOTES:
The highlighted lines are sections of interest to look out for.
The code is heavily commented, so no further insight is necessary. If you have any questions, feel free to leave a comment below.
Once compiled, you should get this as your output for the example cases:
2
0
C# || 3Sum – How To Get All Triplet Combinations In Array Equal To Target Value Using C#

The following is a module with functions which demonstrates how to get all triplet combinations in an array equal to a target value using C#.
1. 3 Sum – Problem Statement
Given an integer array nums, return all the triplets [nums[i], nums[j], nums[k]] such that i != j, i != k, and j != k, and nums[i] + nums[j] + nums[k] == 0.
Notice that the solution set must not contain duplicate triplets.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [-1,0,1,2,-1,-4]
Output: [[-1,-1,2],[-1,0,1]]
Example 2:
Input: nums = []
Output: []
Example 3:
Input: nums = [0]
Output: []
2. 3 Sum – Solution
The following is a solution which demonstrates how to get all triplet combinations in an array equal to a target value.
This solution uses the two pointer technique to find combinations.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 |
// ============================================================================ // Author: Kenneth Perkins // Date: Oct 28, 2021 // Taken From: http://programmingnotes.org/ // File: Solution.cs // Description: Demonstrates how to get 3 numbers equal to target value // ============================================================================ public class Solution { public IList<IList<int>> ThreeSum(int[] nums) { var result = new List<IList<int>>(); // Sort the array Array.Sort(nums); // Set the target value var target = 0; // Loop through numbers for (int index = 0; index < nums.Length; ++index) { // Skip duplicates if (index > 0 && nums[index] == nums[index - 1]) { continue; } // Find all 3 sum combinations that equal the target value var startIndex = index + 1; var endIndex = nums.Length - 1; while (startIndex < endIndex) { // Get the sum var sum = nums[index] + nums[startIndex] + nums[endIndex]; // Sum equals target if (sum == target) { // Add values to results when a target is found var valueStart = nums[startIndex]; var valueEnd = nums[endIndex]; result.Add(new List<int>{nums[index], valueStart, valueEnd}); // Advance past duplicate items to the 'next' values // at the start and end of the array while (startIndex < endIndex && valueStart == nums[startIndex]) { ++startIndex; } while (startIndex < endIndex && valueEnd == nums[endIndex]) { --endIndex; } // Sum is less than target } else if (sum < target) { ++startIndex; // Sum is greater than target } else { --endIndex; } } } return result; } }// http://programmingnotes.org/ |
QUICK NOTES:
The highlighted lines are sections of interest to look out for.
The code is heavily commented, so no further insight is necessary. If you have any questions, feel free to leave a comment below.
Once compiled, you should get this as your output for the example cases:
[[-1,-1,2],[-1,0,1]]
[]
[]
C# || Two Sum II – How To Get Two Numbers In Sorted Array Equal To Target Value Using C#

The following is a module with functions which demonstrates how to get two numbers in a sorted array equal to target value using C#.
1. Two Sum II – Problem Statement
Given a 1-indexed array of integers numbers that is already sorted in non-decreasing order, find two numbers such that they add up to a specific target number. Let these two numbers be numbers[index1] and numbers[index2] where 1 <= index1 < index2 <= numbers.length.
Return the indices of the two numbers, index1 and index2, added by one as an integer array [index1, index2] of length 2.
The tests are generated such that there is exactly one solution. You may not use the same element twice.
Example 1:
Input: numbers = [2,7,11,15], target = 9
Output: [1,2]
Explanation: The sum of 2 and 7 is 9. Therefore, index1 = 1, index2 = 2. We return [1, 2].
Example 2:
Input: numbers = [2,3,4], target = 6
Output: [1,3]
Explanation: The sum of 2 and 4 is 6. Therefore index1 = 1, index2 = 3. We return [1, 3].
Example 3:
Input: numbers = [-1,0], target = -1
Output: [1,2]
Explanation: The sum of -1 and 0 is -1. Therefore index1 = 1, index2 = 2. We return [1, 2].
2. Two Sum II – Solution
The following is a solution which demonstrates how to get two numbers in sorted array equal to target value.
In this solution, Binary Search is used to find the two numbers.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 |
// ============================================================================ // Author: Kenneth Perkins // Date: Oct 28, 2021 // Taken From: http://programmingnotes.org/ // File: Solution.cs // Description: Demonstrates how to get two numbers equal to target value // ============================================================================ public class Solution { public int[] TwoSum(int[] numbers, int target) { var result = new int[2]; var lo = 0; var hi = numbers.Length - 1; while (lo < hi) { var m = lo + (hi - lo) / 2; var sum = numbers[lo] + numbers[hi]; if (sum == target) { result[0] = lo + 1; result[1] = hi + 1; break; } else if (sum < target) { // Determine if mid is less than the remaining value // Increase lo to equal mid if so if (numbers[m] < target - numbers[hi]) { lo = m + 1; } else { lo = lo + 1; } } else { // Determine if mid is greater than the remaining value // Decrease hi to equal mid if so if (numbers[m] > target - numbers[lo]) { hi = m - 1; } else { hi = hi - 1; } } } return result; } }// http://programmingnotes.org/ |
QUICK NOTES:
The highlighted lines are sections of interest to look out for.
The code is heavily commented, so no further insight is necessary. If you have any questions, feel free to leave a comment below.
Once compiled, you should get this as your output for the example cases:
[1,2]
[1,3]
[1,2]
C# || Two Sum – How To Get Two Numbers In Array Equal To Target Value Using C#

The following is a module with functions which demonstrates how to get two numbers in array equal to target value using C#.
1. Two Sum – Problem Statement
Given an array of integers nums and an integer target, return indices of the two numbers such that they add up to target.
You may assume that each input would have exactly one solution, and you may not use the same element twice.
You can return the answer in any order.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [2,7,11,15], target = 9
Output: [0,1]
Output: Because nums[0] + nums[1] == 9, we return [0, 1].
Example 2:
Input: nums = [3,2,4], target = 6
Output: [1,2]
Example 3:
Input: nums = [3,3], target = 6
Output: [0,1]
2. Two Sum – Solution
The following is a solution which demonstrates how to get two numbers in array equal to target value.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 |
// ============================================================================ // Author: Kenneth Perkins // Date: Oct 28, 2021 // Taken From: http://programmingnotes.org/ // File: Solution.cs // Description: Demonstrates how to get two numbers equal to target value // ============================================================================ public class Solution { public int[] TwoSum(int[] nums, int target) { var result = new int[2]; // Use a map dictionary to keep track of the numbers already seen var seen = new Dictionary<int, int>(); // Go through numbers for (int index = 0; index < nums.Length; ++index) { // Subtract the target from the current array index. // The result of this operation is the second number // that is needed to equal the target value int remaining = target - nums[index]; // Check if we have 'seen' this remaining value before if (seen.ContainsKey(remaining)) { result[0] = seen[remaining]; result[1] = index; break; } // Save the number and index seen[nums[index]] = index; } return result; } }// http://programmingnotes.org/ |
QUICK NOTES:
The highlighted lines are sections of interest to look out for.
The code is heavily commented, so no further insight is necessary. If you have any questions, feel free to leave a comment below.
Once compiled, you should get this as your output for the example cases:
[0,1]
[1,2]
[0,1]
C# || How To Generate Unique Subsets From Array With Duplicate Values Using C#

The following is a module with functions which demonstrates how to generate unique subsets from an array with duplicate values using C#.
1. Subsets With Dup – Problem Statement
Given an integer array nums that may contain duplicates, return all possible subsets (the power set).
The solution set must not contain duplicate subsets. Return the solution in any order.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [1,2,2]
Output: [[],[1],[1,2],[1,2,2],[2],[2,2]]
Example 2:
Input: nums = [0]
Output: [[],[0]]
2. Subsets With Dup – Solution
The following is a solution which demonstrates how to generate unique subsets from an array with duplicate values.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 |
// ============================================================================ // Author: Kenneth Perkins // Date: Oct 27, 2021 // Taken From: http://programmingnotes.org/ // File: Solution.cs // Description: Demonstrates how to generate unique permutations // ============================================================================ public class Solution { List<IList<int>> result = new List<IList<int>>(); public IList<IList<int>> SubsetsWithDup(int[] nums) { // Sort array Array.Sort(nums); Generate(nums, 0, new List<int>()); return result; } public void Generate(int[] nums, int startIndex, List<int> combination) { result.Add(new List<int>(combination)); for (int index = startIndex; index < nums.Length; ++index) { // Check to see if this number has been visited if (index > startIndex && nums[index] == nums[index - 1]) { continue; } // Add this number to the combination combination.Add(nums[index]); // Keep generating subsets Generate(nums, index + 1, combination); // Remove last item as its already been explored combination.RemoveAt(combination.Count - 1); } } }// http://programmingnotes.org/ |
QUICK NOTES:
The highlighted lines are sections of interest to look out for.
The code is heavily commented, so no further insight is necessary. If you have any questions, feel free to leave a comment below.
Once compiled, you should get this as your output for the example cases:
[[],[1],[1,2],[1,2,2],[2],[2,2]]
[[],[0]]
C# || How To Generate Subsets From Array With Distinct Values Using C#

The following is a module with functions which demonstrates how to generate subsets from an array with distinct values using C#.
1. Subsets – Problem Statement
Given an integer array nums of unique elements, return all possible subsets (the power set).
The solution set must not contain duplicate subsets. Return the solution in any order.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [1,2,3]
Output: [[],[1],[2],[1,2],[3],[1,3],[2,3],[1,2,3]]
Example 2:
Input: nums = [0]
Output: [[],[0]]
2. Subsets – Solution
The following is a solution which demonstrates how to generate subsets from an array with distinct values.
This solution uses bit manipulation to generate 2^n possibilities based of the array length, and then adds items to the result list if the array index is a valid bit based off of the subset possibilities.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 |
// ============================================================================ // Author: Kenneth Perkins // Date: Oct 27, 2021 // Taken From: http://programmingnotes.org/ // File: Solution.cs // Description: Demonstrates how to generate subsets // ============================================================================ public class Solution { public IList<IList<int>> Subsets(int[] nums) { var result = new List<IList<int>>(); // (2^n possibilities) var possibilities = (1 << nums.Length); // Generate subsets (2^n possibilities) for (int possibility = 0; possibility < possibilities; ++possibility) { var subset = new List<int>(); // Add item to result if index is a valid bit // based off of the subset possibilities for (int index = 0; index < nums.Length; ++index) { if (((possibility >> index) & 1) == 1) { subset.Add(nums[index]); } } result.Add(subset); } return result; } }// http://programmingnotes.org/ |
QUICK NOTES:
The highlighted lines are sections of interest to look out for.
The code is heavily commented, so no further insight is necessary. If you have any questions, feel free to leave a comment below.
Once compiled, you should get this as your output for the example cases:
[[],[1],[2],[1,2],[3],[1,3],[2,3],[1,2,3]]
[[],[0]]
C# || How To Generate Next Permutation From Array Using C#

The following is a module with functions which demonstrates how to generate the next permutation from an array using C#.
1. Next Permutation – Problem Statement
Implement next permutation, which rearranges numbers into the lexicographically next greater permutation of numbers.
If such an arrangement is not possible, it must rearrange it as the lowest possible order (i.e., sorted in ascending order).
The replacement must be in place and use only constant extra memory.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [1,2,3]
Output: [1,3,2]
Example 2:
Input: nums = [3,2,1]
Output: [1,2,3]
Example 3:
Input: nums = [1,1,5]
Output: [1,5,1]
Example 4:
Input: nums = [1]
Output: [1]
2. Next Permutation – Solution
The following is a solution which demonstrates how to generate the next permutation from an array
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 |
// ============================================================================ // Author: Kenneth Perkins // Date: Oct 27, 2021 // Taken From: http://programmingnotes.org/ // File: Solution.cs // Description: Demonstrates how to generate the next permutation // ============================================================================ public class Solution { public void NextPermutation(int[] nums) { // Starting from the end, look for the first index that is not in descending order var startIndex = nums.Length - 2; while (startIndex >= 0) { // Find first decreasing element if (nums[startIndex] < nums[startIndex + 1]) { break; } --startIndex; } if (startIndex >= 0) { // Starting from the end, look for the first element greater than the start index int endIndex = nums.Length - 1; while (endIndex > startIndex) { // Find first greater element if (nums[endIndex] > nums[startIndex]) { break; } --endIndex; } // Swap first and last elements Swap(ref nums[startIndex], ref nums[endIndex]); } // Reverse the array Reverse(nums, startIndex + 1); } private void Reverse(int[] nums, int startIndex) { for (int start = startIndex, end = nums.Length - 1; start < end; ++start, --end) { Swap(ref nums[start], ref nums[end]); } } private void Swap(ref int a, ref int b) { var tmp = a; a = b; b = tmp; } }// http://programmingnotes.org/ |
QUICK NOTES:
The highlighted lines are sections of interest to look out for.
The code is heavily commented, so no further insight is necessary. If you have any questions, feel free to leave a comment below.
Once compiled, you should get this as your output for the example cases:
[1,3,2]
[1,2,3]
[1,5,1]
[1]
C# || How To Generate Unique Permutations From Array With Duplicate Values Using C#

The following is a module with functions which demonstrates how to generate unique permutations from an array with duplicate values using C#.
1. Permute Unique – Problem Statement
Given a collection of numbers, nums, that might contain duplicates, return all possible unique permutations in any order.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [1,1,2]
Output:
[[1,1,2],
[1,2,1],
[2,1,1]]
Example 2:
Input: nums = [1,2,3]
Output: [[1,2,3],[1,3,2],[2,1,3],[2,3,1],[3,1,2],[3,2,1]]
2. Permute Unique – Solution
The following is a solution which demonstrates how to generate unique permutations from an array with duplicate values.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 |
// ============================================================================ // Author: Kenneth Perkins // Date: Oct 27, 2021 // Taken From: http://programmingnotes.org/ // File: Solution.cs // Description: Demonstrates how to generate unique permutations // ============================================================================ public class Solution { private List<IList<int>> result = new List<IList<int>>(); public IList<IList<int>> PermuteUnique(int[] nums) { // Sort Array Array.Sort(nums); Generate(nums, new List<int>(), new bool[nums.Length]); return result; } private void Generate(int[] nums, List<int> combination, bool[] visited) { if (combination.Count == nums.Length) { result.Add(new List<int>(combination)); return; } for (int index = 0; index < nums.Length; ++index) { // Check to see if this number has been visited if (visited[index]) { continue; } else if (index > 0 && nums[index] == nums[index - 1] && !visited[index - 1]) { continue; } // Set that this index has been visited visited[index] = true; // Add this number to the combination combination.Add(nums[index]); // Keep generating permutations Generate(nums, combination, visited); // Unset that this index has been visited visited[index] = false; // Remove last item as its already been explored combination.RemoveAt(combination.Count - 1); } } }// http://programmingnotes.org/ |
QUICK NOTES:
The highlighted lines are sections of interest to look out for.
The code is heavily commented, so no further insight is necessary. If you have any questions, feel free to leave a comment below.
Once compiled, you should get this as your output for the example cases:
[[1,1,2],[1,2,1],[2,1,1]]
[[1,2,3],[1,3,2],[2,1,3],[2,3,1],[3,1,2],[3,2,1]]
C# || How To Generate Permutations From Array With Distinct Values Using C#

The following is a module with functions which demonstrates how to generate permutations from an array with distinct values using C#.
1. Permute – Problem Statement
Given an array nums of distinct integers, return all the possible permutations. You can return the answer in any order.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [1,2,3]
Output: [[1,2,3],[1,3,2],[2,1,3],[2,3,1],[3,1,2],[3,2,1]]
Example 2:
Input: nums = [0,1]
Output: [[0,1],[1,0]]
Example 3:
Input: nums = [1]
Output: [[1]]
2. Permute – Solution
The following is a solution which demonstrates how to generate permutations from an array with distinct values.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 |
// ============================================================================ // Author: Kenneth Perkins // Date: Oct 27, 2021 // Taken From: http://programmingnotes.org/ // File: Solution.cs // Description: Demonstrates how to generate permutations // ============================================================================ public class Solution { private List<IList<int>> result = new List<IList<int>>(); public IList<IList<int>> Permute(int[] nums) { Generate(nums, new List<int>(), new bool[nums.Length]); return result; } private void Generate(int[] nums, List<int> combination, bool[] visited) { if (combination.Count == nums.Length) { result.Add(new List<int>(combination)); return; } for (int index = 0; index < nums.Length; ++index) { // Check to see if this index has been visited if (visited[index]) { continue; } // Set that this index has been visited visited[index] = true; // Add this number to the combination combination.Add(nums[index]); // Keep generating permutations Generate(nums, combination, visited); // Unset that this index has been visited visited[index] = false; // Remove last item as its already been explored combination.RemoveAt(combination.Count - 1); } } }// http://programmingnotes.org/ |
QUICK NOTES:
The highlighted lines are sections of interest to look out for.
The code is heavily commented, so no further insight is necessary. If you have any questions, feel free to leave a comment below.
Once compiled, you should get this as your output for the example cases:
[[1,2,3],[1,3,2],[2,1,3],[2,3,1],[3,1,2],[3,2,1]]
[[0,1],[1,0]]
[[1]]
C# || How To Get Array Combination Sum Equal To Target Value Using C#

The following is a module with functions which demonstrates how to get an array combination sum equal to a target value using C#.
1. Combination Sum – Problem Statement
Given an array of distinct integers candidates and a target integer target, return a list of all unique combinations of candidates where the chosen numbers sum to target. You may return the combinations in any order.
The same number may be chosen from candidates an unlimited number of times. Two combinations are unique if the frequency of at least one of the chosen numbers is different.
It is guaranteed that the number of unique combinations that sum up to target is less than 150 combinations for the given input.
Example 1:
Input: candidates = [2,3,6,7], target = 7
Output: [[2,2,3],[7]]
Explanation:
2 and 3 are candidates, and 2 + 2 + 3 = 7. Note that 2 can be used multiple times.
7 is a candidate, and 7 = 7.
These are the only two combinations.
Example 2:
Input: candidates = [2,3,5], target = 8
Output: [[2,2,2,2],[2,3,3],[3,5]]
Example 3:
Input: candidates = [2], target = 1
Output: []
Example 4:
Input: candidates = [1], target = 1
Output: [[1]]
Example 5:
Input: candidates = [1], target = 2
Output: [[1,1]]
2. Combination Sum – Solution
The following is a solution which demonstrates how to get an array combination sum equal to a target value.
The main idea of this solution is to generate subsets of the different combinations that can be matched together, checking to see if any sum up to equal the target value.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 |
// ============================================================================ // Author: Kenneth Perkins // Date: Oct 26, 2021 // Taken From: http://programmingnotes.org/ // File: Solution.cs // Description: Demonstrates how to get combination sum equal to target // ============================================================================ public class Solution { List<IList<int>> result = new List<IList<int>>(); public IList<IList<int>> CombinationSum(int[] candidates, int target) { Search(candidates, target, 0, 0, new List<int>()); return result; } private void Search(int[] candidates, int target, int currentSum, int currentIndex, List<int> combination) { // Sum is greater than target, exit if (currentSum > target) { return; } // Sum equals target if (currentSum == target) { result.Add(new List<int>(combination)); return; } // Generate subsets for (int index = currentIndex; index < candidates.Length; ++index) { // Add number to combination combination.Add(candidates[index]); // Keep searching for matches Search(candidates, target, currentSum + candidates[index], index, combination); // Remove last item as its already been explored combination.RemoveAt(combination.Count - 1); } } }// http://programmingnotes.org/ |
QUICK NOTES:
The highlighted lines are sections of interest to look out for.
The code is heavily commented, so no further insight is necessary. If you have any questions, feel free to leave a comment below.
Once compiled, you should get this as your output for the example cases:
[[2,2,3],[7]]
[[2,2,2,2],[2,3,3],[3,5]]
[]
[[1]]
[[1,1]]
C# || How To Invert Binary Tree Using C#

The following is a module with functions which demonstrates how to invert a binary tree using C#.
1. Invert Tree – Problem Statement
Given the root of a binary tree, invert the tree, and return its root.
Example 1:

Input: root = [4,2,7,1,3,6,9]
Output: [4,7,2,9,6,3,1]
Example 2:
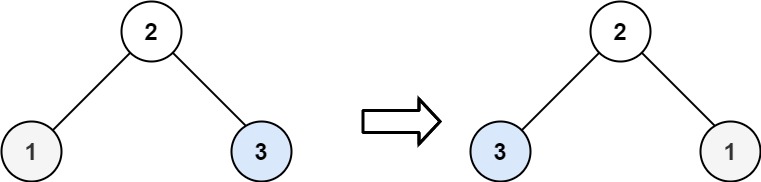
Input: root = [2,1,3]
Output: [2,3,1]
Example 3:
Input: root = []
Output: []
2. Invert Tree – Solution
The following is a solution which demonstrates how to invert a binary tree.
An inverted Binary Tree is simply a Binary Tree whose left and right children are swapped.
This solution:
- Traverses the left subtree
- Traverses the right subtree
- When both trees have been traversed, swap left and right child subtrees
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 |
// ============================================================================ // Author: Kenneth Perkins // Date: Oct 26, 2021 // Taken From: http://programmingnotes.org/ // File: Solution.cs // Description: Demonstrates how to invert a binary tree // ============================================================================ /** * Definition for a binary tree node. * public class TreeNode { * public int val; * public TreeNode left; * public TreeNode right; * public TreeNode(int val=0, TreeNode left=null, TreeNode right=null) { * this.val = val; * this.left = left; * this.right = right; * } * } */ public class Solution { public TreeNode InvertTree(TreeNode root) { Traverse(root); return root; } private void Traverse(TreeNode node) { if (node == null) { return; } // Keep traversing left and right nodes Traverse(node.left); Traverse(node.right); // Root has been visited, swap left and right child nodes var temp = node.left; node.left = node.right; node.right = temp; } }// http://programmingnotes.org/ |
QUICK NOTES:
The highlighted lines are sections of interest to look out for.
The code is heavily commented, so no further insight is necessary. If you have any questions, feel free to leave a comment below.
Once compiled, you should get this as your output for the example cases:
[4,7,2,9,6,3,1]
[2,3,1]
[]
C# || MinStack – How To Implement Minimum Element Stack Using C#

The following is a module with functions which demonstrates how to implement minimum element stack using C#.
1. MinStack – Problem Statement
Design a stack that supports push, pop, top, and retrieving the minimum element in constant time.
Implement the MinStack class:
- MinStack() initializes the stack object.
- void push(int val) pushes the element val onto the stack.
- void pop() removes the element on the top of the stack.
- int top() gets the top element of the stack.
- int getMin() retrieves the minimum element in the stack.
Example 1:
Input
["MinStack","push","push","push","getMin","pop","top","getMin"]
[[],[-2],[0],[-3],[],[],[],[]]Output
[null,null,null,null,-3,null,0,-2]Explanation
MinStack minStack = new MinStack();
minStack.push(-2);
minStack.push(0);
minStack.push(-3);
minStack.getMin(); // return -3
minStack.pop();
minStack.top(); // return 0
minStack.getMin(); // return -2
2. MinStack – Solution
The following is a solution which demonstrates how to implement minimum element stack.
The main idea of this solution is to have a way to keep track of the minimum value every time an item is pushed onto the stack.
When a new value is pushed onto the stack, it is checked against the last minimum to see if the current value is a minimum. Every time a new item is added, we keep track of the minimum value for each push.
In this solution:
- When the Top function is called, the current top value is returned
- When the GetMin function is called, the minimum value at the time the top value was pushed onto the stack is returned
- When the Push function is called, the value and the current minimum value is pushed onto the stack
A list< pair < int, int>> is used to keep track of the current item pushed onto the stack, and the minimum value at the time the item was pushed onto the stack.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 |
// ============================================================================ // Author: Kenneth Perkins // Date: Oct 24, 2021 // Taken From: http://programmingnotes.org/ // File: Solution.cs // Description: Demonstrates how to implement minimum element stack // ============================================================================ public class MinStack { private List<KeyValuePair<int, int>> data; /** initialize your data structure here. */ public MinStack() { // Initialize the list // The pair key is the stack value // The pair value is the current stack minimum value data = new List<KeyValuePair<int, int>>(); } public void Push(int val) { // Determine minimum value. // If the stack is not empty, compare against the last min value var currentMinValue = val; if (data.Count > 0) { currentMinValue = Math.Min(currentMinValue, GetMin()); } // Add new entry to the stack, saving the value and current minimum data.Add(new KeyValuePair<int, int>(val, currentMinValue)); } public void Pop() { data.RemoveAt(data.Count - 1); } public int Top() { // Return the current top value return data[data.Count - 1].Key; } public int GetMin() { // Return the current minimum value return data[data.Count - 1].Value; } }// http://programmingnotes.org/ |
QUICK NOTES:
The highlighted lines are sections of interest to look out for.
The code is heavily commented, so no further insight is necessary. If you have any questions, feel free to leave a comment below.
Once compiled, you should get this as your output for the example cases:
[null,null,null,null,-3,null,0,-2]
C# || How To Find Minimum In Rotated Sorted Array With Duplicates Using C#

The following is a module with functions which demonstrates how to find the minimum value in a rotated sorted array with duplicates using C#.
1. Find Min Duplicates – Problem Statement
Suppose an array of length n sorted in ascending order is rotated between 1 and n times. For example, the array nums = [0,1,4,4,5,6,7] might become:
- [4,5,6,7,0,1,4] if it was rotated 4 times.
- [0,1,4,4,5,6,7] if it was rotated 7 times.
Notice that rotating an array [a[0], a[1], a[2], …, a[n-1]] 1 time results in the array [a[n-1], a[0], a[1], a[2], …, a[n-2]].
Given the sorted rotated array nums that may contain duplicates, return the minimum element of this array.
You must decrease the overall operation steps as much as possible.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [1,3,5]
Output: 1
Example 2:
Input: nums = [2,2,2,0,1]
Output: 0
2. Find Min Duplicates – Solution
The following is a solution which demonstrates how to find the minimum value in a rotated sorted array with duplicates.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 |
// ============================================================================ // Author: Kenneth Perkins // Date: Oct 22, 2021 // Taken From: http://programmingnotes.org/ // File: Solution.cs // Description: Demonstrates how to find the minimum value in a sorted array // ============================================================================ public class Solution { public int FindMin(int[] nums) { var lo = 0; var hi = nums.Length - 1; // In cases where the front and back of the array are the // same (ex: [1,19,28,87,91,0,1,1,1]), decrease the end of the array while (nums[lo] == nums[hi] && lo < hi) { --hi; } // Perform binary search while (lo < hi) { var mid = lo + (hi - lo) / 2; // Midpoint element is greater than right side of array, so // the minumum element is somewhere on the right side of array. // Advance lo value to equal midpoint + 1 if (nums[mid] > nums[hi]) { lo = mid + 1; // Midpoint element is less than right side of array, so // the minumum element is somewhere on the left side of array. // Decrease hi value to equal midpoint } else if (nums[mid] < nums[hi]) { hi = mid; // Duplicate element found (nums[mid] == nums[hi]) } else { --hi; } } return nums[lo]; } }// http://programmingnotes.org/ |
QUICK NOTES:
The highlighted lines are sections of interest to look out for.
The code is heavily commented, so no further insight is necessary. If you have any questions, feel free to leave a comment below.
Once compiled, you should get this as your output for the example cases:
1
0












